Sometimes Management Servers have to be removed from a Service Manager Management Group. This last blog post of the series will explain all the needed steps.
Dealing with multiple Management Servers series:
- Part 1/3: Install an additional Management Server
- Part 2/3: Load Balance Management Servers
- Part 3/3: Decommission old Management Servers (this post)
Step 1 – Reconfigure the Workflow Server
First of all we have to find out if the Management Server that should be eliminated runs the Service Manager workflows. Normally this happens on the first Management Server that was installed in the Management Group – but of course it’s possible that this has been changed before. So let’s check this by using a simple SQL Query against the Service Manager database.
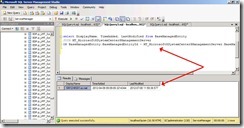
select DisplayName, [PrincipalName] from [MTV_Computer]
where [BaseManagedEntityId]=
(SELECT ScopedInstanceId
FROM dbo.[ScopedInstanceTargetClass]
WHERE [ManagedTypeId] = dbo.fn_ManagedTypeId_MicrosoftSystemCenterWorkflowTarget()
)
If the script output shows the server that you want to eliminate then this needs to be changed first by executing a stored procedure. But before executing the script stop all Service Manager services on the server that will be the new Workflow Server.
Not execute the script against the Service Manager database.
EXEC p_PromoteActiveWorkflowServer ‘<FQDN of your server>’
Restart the Service Manager services and you’re done. Now we are ready to remove the Management Server.
Step 2 – Uninstall the Management Server
First lets check what Management Servers are installed in the Service Manager Management Group by executing a simple SQL script.
select DisplayName, TimeAdded, LastModified from BaseManagedEntity
JOIN MT_Microsoft$SystemCenter$ManagementServer
ON BaseManagedEntity.BaseManagedEntityId = MT_Microsoft$SystemCenter$ManagementServer.BaseManagedEntityId
Now uninstall the Service Manager Management Server by using the “Programs and Features” in the Control Panel.
After uninstalling, we have to remove the Management Server from the Management Group by using a Powershell Script that is based on the smlets (or in a slightly different way by using the Service Manager Powershell Module).
import-module smlets
$class = get-scsmclass Microsoft.SystemCenter.ManagementServer$
$ms = get-scsmobject –class $class –filter “displayname = sm12-ms02.sc.net” (name of your MS here)
$ms | remove-scsmobject –force
Now the Management Server should be removed from the Management Group. You can check if this step was successful by executing the above SQL script again.
Step 3 – Post-Uninstallation Tasks
When the Management Server is completely decommissioned you should to delete the computer account in ADDS or at least delete the Service Connection Point (SCP). The SCP is a child object of the computer account. When the removal of the Management Server was successful, the SCP should have been removed automatically.
(Example of SCP of a still active Management Server)
(SCP of uninstalled Management Server is gone)
Now remove the Service Principal Names (SPN) for the uninstalled Management Server.
- setspn.exe –D MSOMSdkSvc/ServernameNetBIOS Domain\ServiceAccount
- setspn.exe –D MSOMSdkSvc/ServernameFQDN Domain\ServiceAccount
Check if the SPNs have been deleted successfully.
- setspn.exe –L Domain\ServiceAccount
Because users will not be able to connect to the uninstalled Management Server anymore it can make sense to deploy a package or use GPOs to change the server name the console connects to. This can be done by settings a simple registry key value.
- HLCU\Software\Microsoft\System Center\2012\Service Manager\Console\User Settings\SDKServiceMachine
After all those steps you have removed the Management Server from the Management Group and have done the needed cleaning.
cu later, Marcel













when i run last command $ms | remove-scsmobject –force i get an error
Remove-SCSMObject : Cannot bind argument to parameter ‘SMObject’ because it is null.
Hey
It seems that the command to get the Management Server Object is somehow wrong and therefore the $MS variable is empty. Try to get the MS correctly, then this should work.
regards
Marcel
Multiple management server can be efficient.When we want to work with a group of machines at one time, then there are some techniques and tools which makes management of multiple servers easy and efficient.
Hi Marcel,
I didn’t have enough time to look into it, but it looks like the get-scsmobject and remove scsm-object are gone in SCSM 2012 R2. Am I missing something ?
It’s still there in the smlets module.
Hi Marcel,
I have recently tried this technique for installing/promoting/migrating to a new Service Manager Management Server, this had completely destroyed our environment.
I believe one key step you are missing is that the SMS database Encryption Keys need to be installed to the new management server machine BEFORE installing the secondary management server.
If you do not do this step the secondary management server will still work until you uninstall SCSM from the demoted primary management server box.. once you do this the new server does not have the encryption keys to authenticate with the database and the SDK service/workflows die within a few hours.
The only resolution is a disaster recovery on the initial management server and restore the database prior to any changes
Have you successfully been able to decommission an old primary and migrate to a new primary without doing such?
thanks
nick.
On a SCSM 2012R2 system, it is necessary to include “-Name” in the powershell command that defines the $class variable, and remove the $ from the end of the management server class:
import-module smlets
$class = get-scsmclass -Name Microsoft.SystemCenter.ManagementServer
$ms = get-scsmobject –class $class –filter “displayname = sm12-ms02.sc.net” (name of your MS here)
$ms | remove-scsmobject –force
Has any one tried this method and decommissioned the old primary server after deploying secondary mgmt server and promote it to primary server successfully???